2024: A Year of Progress in Medical Science
The year 2024 has witnessed remarkable advancements across various domains of medical science, offering promising new avenues for diagnosis, treatment, and disease prevention. From revolutionary weight-loss drugs to the growing influence of artificial intelligence, researchers have made significant strides in addressing some of the most pressing health challenges facing humanity. This summary explores some of the key breakthroughs and areas of focus that shaped the medical landscape in 2024.
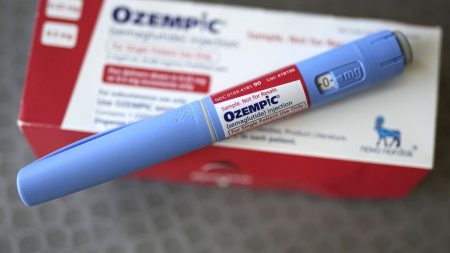
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Expanding Benefits Beyond Weight Loss
GLP-1 receptor agonists, initially developed for type 2 diabetes, have emerged as game-changers in the fight against obesity. Drugs like semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy) have demonstrated remarkable efficacy not only in weight management but also in reducing cardiovascular events like stroke and heart attack. Further research has linked these drugs to decreased kidney failure risk, while tirzepatide, another drug in the same class, has shown promise in mitigating the severity of sleep apnea. The long-term effects and sustainability of these benefits remain under investigation, as scientists explore whether continued drug use is necessary to maintain weight loss and assess the potential for long-term consequences.
HIV Prevention: A Paradigm Shift with Injectable Therapy
A groundbreaking twice-yearly injectable HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) has demonstrated superior efficacy compared to traditional daily oral pills. Clinical trials have revealed remarkable success, with no women contracting HIV in one study and a 96% effectiveness rate in preventing infections among men in another. This innovative approach offers a more convenient and effective alternative to daily medication, potentially revolutionizing HIV prevention strategies and improving adherence rates, particularly crucial for the millions globally who lack access to treatment.
Alzheimer’s Disease: Early Detection and Novel Treatments
A highly accurate blood test, boasting a 90% accuracy rate in identifying Alzheimer’s disease, has simplified the diagnostic process for this debilitating neurodegenerative condition. This eliminates the need for invasive cerebrospinal fluid sampling or PET scans, making early detection more accessible. Furthermore, the approval of new treatments like Lecanemab, which has demonstrated efficacy in slowing cognitive decline, provides a glimmer of hope for patients and their families, marking a significant step forward in Alzheimer’s management.
Artificial Intelligence and Cancer Therapies: Personalized Approaches
Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force in medicine, particularly in cancer diagnostics and treatment. Research continues to explore the potential of AI in enhancing diagnostic accuracy, while personalized cancer therapies, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors and customized vaccines, hold immense promise for improving patient outcomes. The UK’s National Health Service’s trial for personalized cancer vaccines exemplifies the ongoing efforts to tailor treatments to individual patient profiles, maximizing efficacy and minimizing adverse effects.
Lingering Effects of COVID-19 and the Impact of Climate Change
The long-term health consequences of COVID-19, particularly long COVID, which can persist for years, remain a significant concern. Studies investigating the link between ultra-processed foods and various health problems underscore the importance of dietary factors in disease prevention. Furthermore, the impact of climate change on human health has become a central research focus, with growing evidence linking air pollution to infertility and noise pollution to female infertility. The climate impact of the healthcare industry itself is also under scrutiny.
Emerging Infectious Diseases and Global Health Security
The emergence of avian influenza (H5N1) and other infectious disease outbreaks highlight the ongoing threat posed by zoonotic diseases and the need for robust global health security measures. Further research is crucial to understand the dynamics of these outbreaks, develop effective countermeasures, and strengthen international collaboration to prevent future pandemics. The confluence of environmental changes, human behavior, and global interconnectedness underscores the complex interplay of factors influencing emerging infectious diseases and the importance of proactive surveillance and preparedness.