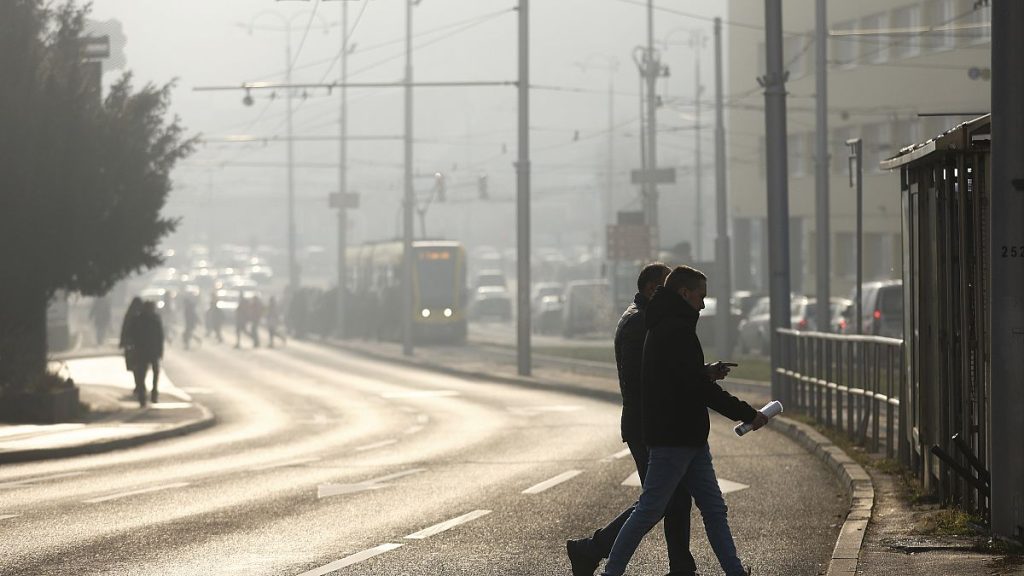
Air pollution, a significant environmental health threat, poses a disproportionate risk across Europe. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5), a mixture of dust, smoke, and soot, contributed to an estimated 239,000 premature deaths in 2021, highlighting the urgent need for effective mitigation strategies. While the entire continent grapples with this challenge, the burden falls heavier on specific regions, revealing a stark east-west divide largely correlated with economic disparities. Central and Eastern European countries experience the highest PM2.5-related mortality rates, primarily due to residential coal burning and agricultural activities. Conversely, western and southern Europe, particularly major cities, face higher nitrogen dioxide (NO2) pollution, largely from vehicle emissions and industry. This disparity underscores the complex interplay of socioeconomic factors, energy sources, and urban development in shaping air pollution patterns.
The World Health Organization (WHO) revised its air quality guidelines in 2021, lowering acceptable thresholds for PM2.5 and NO2. The European Union subsequently introduced stricter regulations aimed at aligning with WHO standards by 2030, mandating member states to monitor key pollutants and empowering citizens to challenge governmental inaction. Although the EU projects a 55% reduction in PM2.5-related deaths by 2030, air pollution and climate change remain growing public health concerns. Evolving scientific understanding reveals air pollution’s adverse health effects at lower concentrations than previously thought, implying that even substantial reductions may not yield proportionally decreased health impacts. This necessitates a continuous reassessment of mitigation strategies and emphasizes the importance of implementing preventative measures.
The contrast in pollution sources between eastern and western Europe requires tailored interventions. Residential heating practices in the east demand a shift towards cleaner energy sources, while tackling traffic and industrial emissions remains crucial in the west. Denmark’s pioneering initiative to implement a carbon tax on livestock farming in 2030 exemplifies proactive measures towards mitigating agricultural emissions. Similarly, the EU’s updated directive empowering citizens to hold governments accountable for air quality standards demonstrates a commitment to regulatory enforcement and public health protection. These varied approaches highlight the need for context-specific solutions recognizing regional differences in pollution sources and socioeconomic factors.
Beyond regulatory measures, addressing the complex interplay of environmental factors is crucial. Air pollution often coexists with other health hazards like noise pollution, lack of green spaces, and extreme heat, exacerbating the overall impact on human health. These interconnected challenges require integrated solutions that consider urban planning, environmental protection, and public health. Improving urban design to incorporate green spaces can mitigate the effects of both air pollution and extreme heat while also promoting mental well-being. Reducing traffic congestion not only lowers NO2 levels but also decreases noise pollution, demonstrating the potential for synergistic benefits from multi-pronged approaches.
Moreover, recognizing the intertwined nature of air pollution and climate change is essential for effective long-term solutions. As climate change intensifies extreme heat events, it exacerbates the health risks associated with air pollution. Tackling these challenges simultaneously requires a transition to sustainable energy sources, promoting energy efficiency, and adopting climate-resilient urban planning strategies. Integrating climate change considerations into air pollution mitigation efforts ensures a more comprehensive and effective response to these interconnected environmental health threats. This integrated approach recognizes the long-term implications of both air pollution and climate change on human health and emphasizes the need for sustainable and resilient solutions.
Ultimately, addressing air pollution requires a multifaceted approach that combines regulatory measures, technological advancements, and behavioral changes. Strengthening air quality standards, enforcing regulations, and investing in pollution monitoring are vital steps. Promoting the adoption of cleaner technologies in industries, transportation, and residential heating can significantly reduce emissions. Encouraging sustainable practices, such as active transportation and reduced energy consumption, can also contribute to cleaner air. By combining these strategies, Europe can move towards a healthier and more sustainable future, addressing the complex challenge of air pollution effectively and protecting public health. This integrated approach recognizes the shared responsibility of governments, industries, and individuals in creating a cleaner and healthier environment for all.