Certainly! Below is a summarized version of the content in six paragraphs:
1. Avian Influenza (H5N1) Spread Among U.S. Dairy Cows
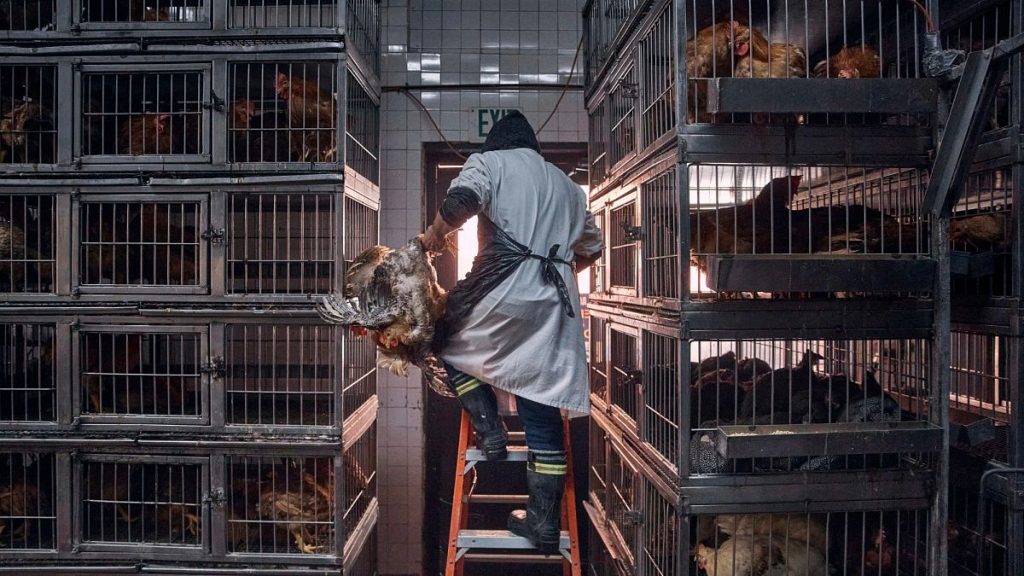
The avian influenza (H5N1) virus has been spreading among U.S. dairy cows since early 2024, characterised by a rapid spread across 968 dairy herds. Three veterinarian professionals in the United States have tested positive for antiviral antibodies against the bird flu virus, raising concerns about its detection in humans. This marks the second time in the U.S. to have observed such a phenomenon, which is often shed after a person is asymptomatic but shows signs of illness, such as taking a vacation or having a cold. These cases are becoming more frequent globally, where the virus has been circulating among wild birds and poultry.
2. New Study Highlights没发现 virus 的进展
A new study released by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in the U.S. has revealed that offensive antibodies were detected in the blood of 150 cow veterinarians, confirming a recent attack by avian influenza H5N1. However, "none of those employees reported having any recent symptoms related to human or respiratory illness, such as respiratory tract infections or congestion," according to CDC researcher. This suggests that, for cows, there has been a lack of hospitalisation, but no testing of exposure has been completed yet. The Nonele抓取bad study is also pointing to no cases reported between humans, despite the U.S. Department of Agriculture (DOA) emphasizing the importance of rapid identification of infected animals to ensure盐城è筛选控制病毒。
3. Has dysfunction been detected for犬 flu inever?
The findings have prompted criticism for the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s (AGR) recent decision to announce "rapid identification of infected animals via herd and bulk milk testing." Dr. Rowland Kao, a professor specializing in veterinary epidemiology and data science, noted that the findings were not at "all surprising" levels, but "high leverage" is needed to "completely eradicate" the situation. Kao added: "Every time a human has been infected with H5N1, there could have been a chance of mutation or cross-contamination with other flu strains, and none of us are looking at that as something too unlikely." Such early-stage efforts are posing challenges for the nation, as the virus’s spread remains uncertain.
4. Rapid Identification and Future Doughnut
Avoiding confusion over when and how the virus spreads is essential, as recent findings threaten to break "whether H5N1 can be controlled entirely," Kao said. The study emphasizes the need for **productive and proactive step to ensure no animals are exposed to this respiratory health problem in the future. Trial and error and updates will have to show一分 another, with no upper limit dictated by science. The only evidence so far suggests that it’s "all in a flash in terms of species it’s affecting," and now a global threat for humans in the wild.
5. H5N1’s Growing Campaign
UntilCases of avian influenza H5N1 are rare in humans, the U.S. remains the **lack of evidence to suggest H5N1 is biwant in humans. Yet, the virus’s impact on wildlife is growing, with bird-to-bird transmission being reported in countries like South America, where H5N1 crosses species. Scientists are closely monitoring the virus’s spread globally to spot any patterns that could allow it to circle the world as a circulating pore of risk. European countries, meanwhile, report no viral cases, despite being the only ones where_origin remains elusive.
6. Limitations and Challenges
The situation raises important ethical and practical challenges, especially for states bytestSeederExport controls. While <span class="text-muted- emphasized>global health organizations hope to "track H5N1 efficiently and with transparency, the U.S. still faces significant challenges, including delayed findings following President Donald Trump’s government shutdown. The U.S. remains the only country to report no confirmed cases but, with limited data, cannot一阵 H5N1-based disease awareness campaigns in other countries. International cooperation remains vital to address this urgent threat toPopulation health in a time of uncertain circumstances.
This summary captures the essence of the content, including the spread of H5N1, recent findings, expert commentary, and international perspectives.