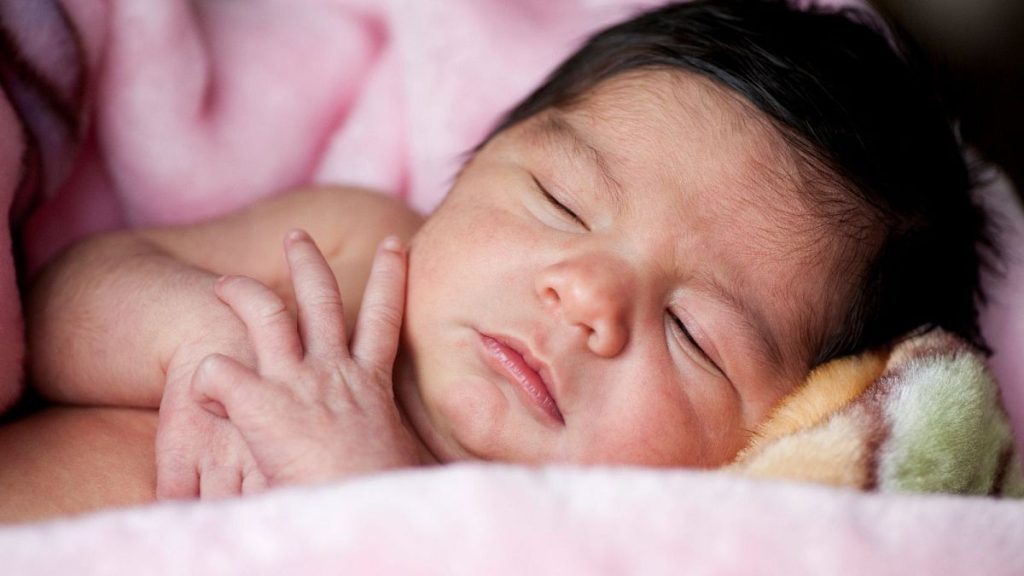
The emergence of “werewolf syndrome,” a rare condition medically known as hypertrichosis, in a cluster of infants across Europe has sparked a significant investigation into the potential link with parental use of minoxidil, a common hair loss treatment. Hypertrichosis, characterized by abnormal and excessive hair growth beyond the scalp, can manifest as full-body coverage or localized patches. The investigation, spearheaded by the Pharmacovigilance Centre of Navarre (CFN) in Spain, revealed a concerning correlation between affected babies and parents using topical minoxidil solutions. This discovery underscores the critical importance of understanding the potential risks associated with commonly used medications, particularly when it comes to vulnerable populations like infants.
The initial case that triggered the investigation involved a baby who developed excessive hair growth on their back, legs, and thighs over a two-month period. The baby’s father, their primary caregiver during this time, had been using a topical minoxidil solution to treat hair loss. This initial observation prompted the CFN to delve deeper, conducting a thorough review of similar cases reported within the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System and the European Medicines Agency’s (EMA) EudraVigilance databases. This broader investigation revealed a pattern of hypertrichosis cases in infants across Europe, all linked to caregivers using topical minoxidil. Remarkably, in the initial case and subsequent ones, the cessation of contact with the minoxidil solution led to a complete regression of the hypertrichosis symptoms in the affected infants.
The investigation highlighted the vulnerability of infants to topical medications due to their thinner and more sensitive skin. This increased permeability allows for greater absorption of substances applied to the skin, potentially leading to unintended side effects. The CFN proposed two likely pathways for minoxidil transfer from caregiver to infant: oral ingestion or direct skin contact. The oral route could involve the infant inadvertently ingesting traces of minoxidil residue left on the caregiver’s hands or through contaminated objects. Direct skin contact, particularly during close physical interaction like cuddling or holding, could lead to the infant’s skin absorbing the medication. This understanding of potential transmission routes emphasizes the importance of careful handling and application of topical medications, especially in households with infants.
The findings of this investigation led to a crucial update in the product information for minoxidil-containing medications. The European Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC), recognizing the potential risk to infants, mandated the inclusion of specific warnings about the possibility of excessive hair growth in babies following contact with areas where minoxidil has been applied. This proactive measure aims to raise awareness among users and healthcare professionals, emphasizing the need for precautionary measures to prevent unintended exposure in infants. The updated product information serves as a critical tool in promoting safe medication practices and protecting vulnerable populations.
The cases of “werewolf syndrome” linked to minoxidil exposure in infants highlight the importance of pharmacovigilance, the continuous monitoring of drug safety. The prompt investigation and subsequent regulatory action demonstrate the effectiveness of these systems in identifying and mitigating potential risks associated with medications. This incident serves as a reminder of the complex interplay between medication use, individual susceptibility, and environmental factors, especially when considering the unique vulnerabilities of infants. The ongoing vigilance and proactive measures taken by regulatory bodies are essential for ensuring the safe and effective use of medications.
This incident also underscores the need for clear and readily accessible information about medication use and potential side effects. Empowering patients and caregivers with accurate and comprehensive information allows them to make informed decisions about their health and the health of their children. Open communication between healthcare providers, patients, and regulatory agencies is crucial for fostering a safe and effective medication landscape. The minoxidil-related hypertrichosis cases serve as a compelling example of the importance of continuous monitoring, proactive risk assessment, and effective communication in ensuring medication safety, particularly for vulnerable populations.