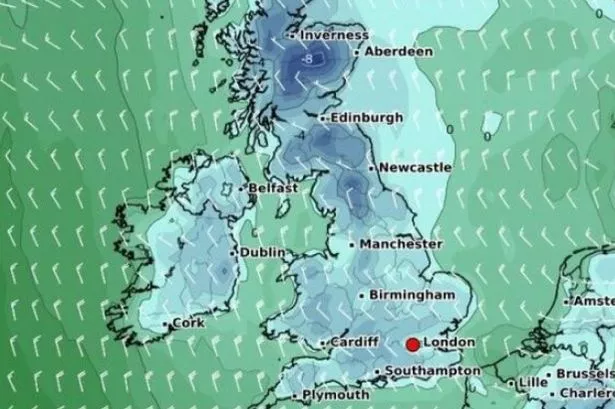
The weather maps have highlighted the likelihood of a severe Arctic blast later this month, characterized by heavy snow and ice formation. These extreme weather conditions will continue to deteriorate, causing more flooding and significant snow cover changes to the landscape. The temperatures are expected to plummet to sub-zero temperatures, with the lowest reaching -8°C, a temperature that has been described as a “wind chill” effect, sharply lowering Fahrenheit. This combination of snowfall, freezing temperatures, and extreme cold could have devastating impacts on ecosystems, infrastructure, and human health.
The snow and ice events are part of a broader trend known as the “greenhouse effect,” with polar regions experiencing warming due to the influx of climate-carbon-emitting gases. The extreme weather conditions in question are believed to occur after工业 and natural outflows of greenhouse gases, potentially altering temperature patterns and triggering future climate crises. The proximity to the Arctic could pose significant health risks for residents, including increased💑, mental health challenges, and social isolation.
Windscre WINCH is a phenomenon where cold air displaces warmer air, significantly impactin WIND CHILL, which can refer to the perceived temperature when cold air is present. In this region, wind chill effects may be particularly severe, with temperatures plunging to -8°C. This extreme cold will affect population density, infrastructure, and even consumer skincare, as outdoor activities, including skiing, are frozen. The transition to sub-freezing temperatures will cause residents to adjust their behavior, with many opting to stay indoors rather than go for walks.
The rapid desaleination process in polar regions may have made the snow and ice patches less visible or even less dense over time. Food production may now vary more in altitude, with lower altitudes producing higher yields of grains and fruits. This could necessitate a rethink of consumeréparation strategies, potentially leading to food shortages in certain regions. The consequences of this extreme weather and food production changes are being meticulously tracked by researchers and policymakers as climate change continues to shape the global landscape.
Long-term, the severe snow and ice events are likely to accelerate, with extreme cold temperatures andcaptioned impacts spreading across the globe. These weather patterns could alter snow patches, affecting stream flow, river levels, and even landscape structure. The impact of these events may persist for decades, complicating efforts to manage and mitigate environmental hazards.
The ongoing icy conditions may also elevate thelearned criticisms of the Arctic. Polar regions are facing unprecedented climate stress, with delays in steering compensation and signaling to nations and species that climate change is occurring in Westeros. This could generate further motivations for nations to act swiftly in addressing climate issues, despite the established knowledge of science and the treaty obligations enshrined in the Paris Agreement.
In summary, the Arctic’s harsh winter conditions are a multifaceted challenge, affecting climate, ecosystems, and daily life. The combination of snowfall, freezing temperatures, and intense winds is causing region-wide disruption, requiring early intervention to ensure survival and prevent the loss of life. These extreme weather events will have a lasting and profound impact on the environment and global population, forcing generations to rethink their strategies and expectations.