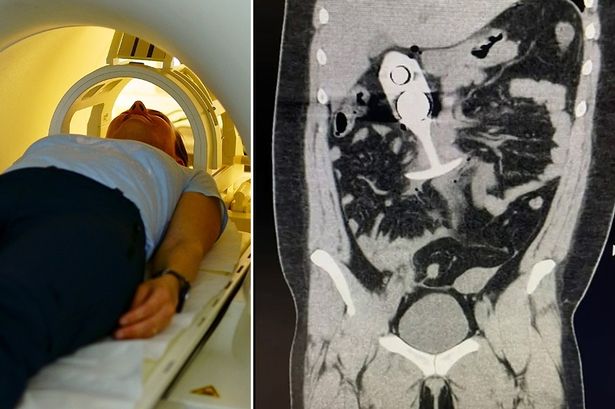
The incident involving a 22-year-old woman and a retained silicone butt plug during an MRI scan underscores the critical importance of open communication between patients and healthcare providers, particularly when undergoing medical imaging procedures. While seemingly embarrassing or inconsequential, withholding information about foreign objects, especially those made of magnetically susceptible materials, can have significant and potentially dangerous repercussions. In this case, the woman’s failure to disclose the presence of the butt plug led to its forceful displacement within her rectum due to the powerful magnetic fields generated by the MRI machine. This resulted in rectal perforation, a serious medical condition requiring immediate surgical intervention and prolonged recovery. This incident highlights the need for clear and unambiguous pre-MRI screening protocols that emphasize the importance of disclosing all implanted devices, foreign objects, and even seemingly innocuous items like body jewelry or intimate accessories.
MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging, harnesses powerful magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images of the body’s internal structures. The intense magnetic field within the MRI scanner exerts a strong attractive force on ferromagnetic objects, which are materials strongly attracted to magnets. While silicone, the material composing the woman’s butt plug, is not ferromagnetic, it is still susceptible to magnetic forces, especially within the extremely high magnetic field environment of an MRI machine. This susceptibility can lead to the object moving or shifting, potentially causing internal damage, as seen in this case. The force exerted on an object within the MRI scanner depends on several factors, including the strength of the magnetic field, the size and shape of the object, and the material’s magnetic susceptibility.
The rectal perforation experienced by the woman is a serious complication that can lead to a range of adverse health outcomes. A perforation refers to a tear or hole in the rectal wall, allowing intestinal contents to leak into the abdominal cavity. This can result in peritonitis, a life-threatening infection of the lining of the abdominal cavity. The subsequent surgical intervention required to repair the perforation and address the infection is often complex and carries its own set of risks, including bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding organs. Moreover, recovery from rectal perforation can be lengthy and involve significant pain, discomfort, and potential long-term bowel dysfunction.
This incident underscores the crucial role of patient education in ensuring the safety and efficacy of medical imaging procedures. Patients must be informed about the potential risks associated with MRI scans, particularly the dangers of undisclosed foreign objects. Pre-MRI questionnaires and interviews should be comprehensive and explicitly inquire about any implants, devices, or objects within the body, regardless of perceived relevance. Clear and accessible information about the MRI procedure, including its underlying principles and potential hazards, can empower patients to make informed decisions and actively participate in their own safety. It’s essential to create a non-judgmental environment where patients feel comfortable disclosing potentially embarrassing information without fear of stigma or reprimand.
Furthermore, healthcare professionals play a pivotal role in facilitating effective communication and ensuring patient safety during MRI procedures. Radiologists and MRI technicians should be trained to conduct thorough pre-scan assessments and effectively communicate the importance of disclosing all relevant information. They should also be adept at creating a supportive and understanding atmosphere where patients feel comfortable asking questions and expressing concerns. Implementing standardized and comprehensive pre-MRI checklists can help minimize the risk of overlooking critical information and ensure that all necessary safety precautions are taken.
In conclusion, the case of the 22-year-old woman and the retained butt plug during an MRI scan serves as a stark reminder of the potential consequences of inadequate communication and incomplete disclosure of information during medical procedures. It emphasizes the need for robust patient education, comprehensive pre-MRI screening protocols, and effective communication between patients and healthcare providers. By prioritizing patient safety, promoting open communication, and fostering a culture of trust and understanding, we can strive to minimize the occurrence of such incidents and ensure the safe and effective use of MRI technology. This incident serves as a valuable learning opportunity for the medical community to refine and strengthen its safety protocols and ensure that all patients receive the highest standard of care. The emphasis must be on creating a collaborative environment where both patients and healthcare providers actively contribute to creating a safe and effective medical experience.